Describe How Enzymatic Actions Function as Defense Mechanisms
10Explain seven innate nonspecific defense mechanisms. 13List the major effects of inflammation and explain why each occurs.
Outline Of Antioxidant Defense Mechanisms In Plants A Types Of Download Scientific Diagram
Mechanism of enzyme action.
. Outline the four principal mechanisms by which enzymes achieve catalysis. Louis Pasteur recognized in 1860 that enzymes were essential to fermentation but assumed that their catalytic action was. Describe how enzymatic actions function as defense mechanisms against pathogens.
1 5 Describe how enzymatic actions function as defense mechanisms. Enzymes provide a chemical barrier to pathogens. 395 Enzymes in body fluids provide a chemical barrier to pathogens.
Inhibits or kills bacteria. Enzyme Production and Purification. Enzyme structure and function.
Anonymous Answered question January 5 2021. Precise mechanisms targeting specific pathogens provide _____ specific defense. Enzymes and activation energy.
Disintegration of the complex molecule to give the product. Nearly all enzymes are proteins although some catalytically active RNA molecules have been identified. 625 13 Define species resistance.
Induced fit model of enzyme catalysis. Co-factors co-enzymes and vitamins. Outline the underlying principles of enzyme-linked immunoassays.
E S ES EP E P. 626 16 Distinguish. 14Describe how enzymatic actions function as.
Enzymes in body fluids provide a chemical barrier to pathogens. These cookies ensure basic functionalities and security features of the website. Kills bacteria by attacking cell wall.
1 5 Describe how enzymatic actions function as defense mechanisms. Chemicals and enzymes in body fluids. Combining of enzyme and the reactantsubstrate.
Necessary cookies are absolutely essential for the website to function properly. Name two mechanical barriers to infection. Defense mechanisms that prevent the entry of many types of pathogens and destroy them if they enter provide _____ nonspecific defense.
Describe how an induced fit facilitates substrate recognition and catalysis. Oleic acid from sebum and skin microbiota. Explain how coupling an enzyme to an NADP-dependent dehydrogenase can simplify assay of its activity.
Introduction to enzymes and catalysis. Enzymes require optimum pH specific for each enzyme. Thus the whole catalyst action of enzymes is summarized as.
For instance a suitable analogy to describe Induced fit model would be that of a hand changing the shape of the glove as the individual put on the glove. An enzyme attracts substrates to its active site catalyzes the chemical reaction by which products are formed and then allows the products to dissociate separate from the enzyme surface. In the protoplasm enzymes exist as hydrophilic colloids.
Describe how enzymatic actions function as defense mechanisms against pathogens Enzymes provide a chemical barrier to pathogens. Gastric juice for example contains the protein-splitting enzyme pepsin and has a low pH due to hydrochloric acid in the stomach. 626 14 Identify the barriers that provide the bodys first line of defense against infectious agents.
Describe how enzymatic actions function as defense. Describe the structure and functions of the spleen. The mechanism of enzymatic action.
Due to colloidal nature they are isolated by dialysis. An enzyme attracts substrates to its active site catalyzes the chemical reaction by which products are formed and then allows the products to dissociate separate from the enzyme surface. 626 15 Describe how enzymatic actions function as defense mechanisms against pathogens.
Describe how enzymatic actions function as defense mechanisms. The amino acids which make up the active site are moulded into precise shape which enable the enzyme to perform its catalytic function most efficiently. This is the currently selected item.
Lowers pH to inhibit pathogens. Describe the mechanism of enzyme action. Distinguish between specific and nonspecific body defenses against infection.
The mechanism of enzymatic action. Describe the structure and functions of the thymus. Describe how enzymatic actions function as defense mechanisms against pathogens.
The enzyme action basically happens in two steps. By splitting components of the pathogen or decreasing the pH the enzyme can have lethal effects on pathogens. Enzymes act catalysts are required in small amount highly specific act best at a temperature between 25 - 40C and at low temperature action slows down and at high temperature get denatured.
Precise mechanisms targeting specific pathogens provide. 3 List three types ofT cells and describe the function of each in the immune response. The combination formed by an enzyme and its substrates is called the enzymesubstrate complex.
Provides oil barrier protecting hair follicle pores from pathogens. Acid in stomach urine and vagina. 12Identify the mechanical barriers that provide the bodys first line of defense against infectious agents.
ES ES Step 2. By splitting components of the pathogen or decreasing the pH the enzyme can have lethal effects on pathogens. Defense mechanisms are behaviors people use to separate themselves from unpleasant events actions or thoughts.
What may cause an infection. These psychological strategies may help people put distance between themselves and. The relative concentration of enzyme and substrate affect the velocity of.
Solution for Describe how enzymatic actions function as defense mechanisms. Sebum from sebaceous glands. Enzyme biological catalystThe term enzyme comes from zymosis the Greek word for fermentation a process accomplished by yeast cells and long known to the brewing industry which occupied the attention of many 19th-century chemists.
Properties and Mechanism of Enzyme Action. Six types of enzymes. Explain what is meant by species resistance.

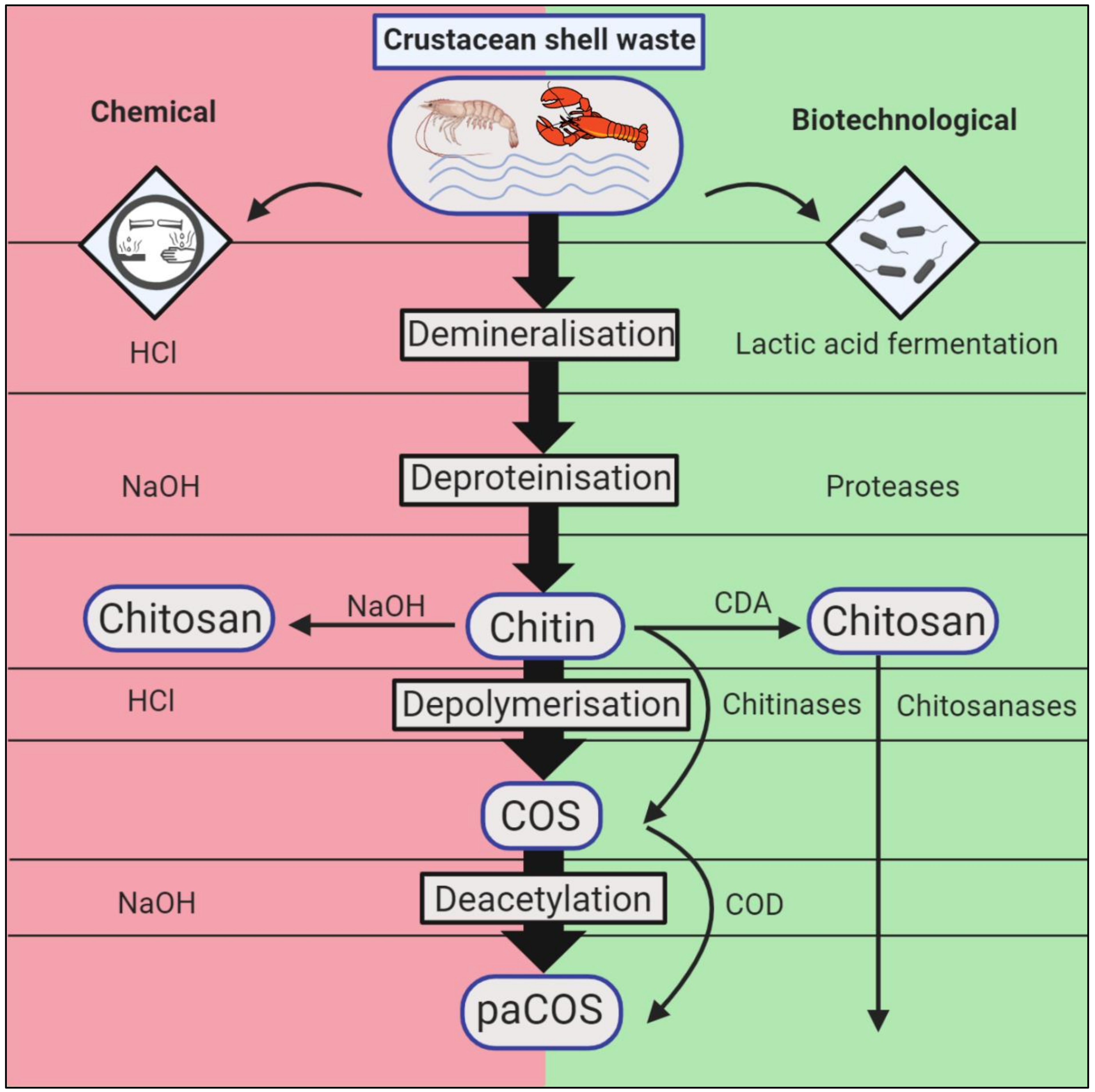
Marine Drugs Free Full Text Enzymatic Modification Of Native Chitin And Conversion To Specialty Chemical Products Html

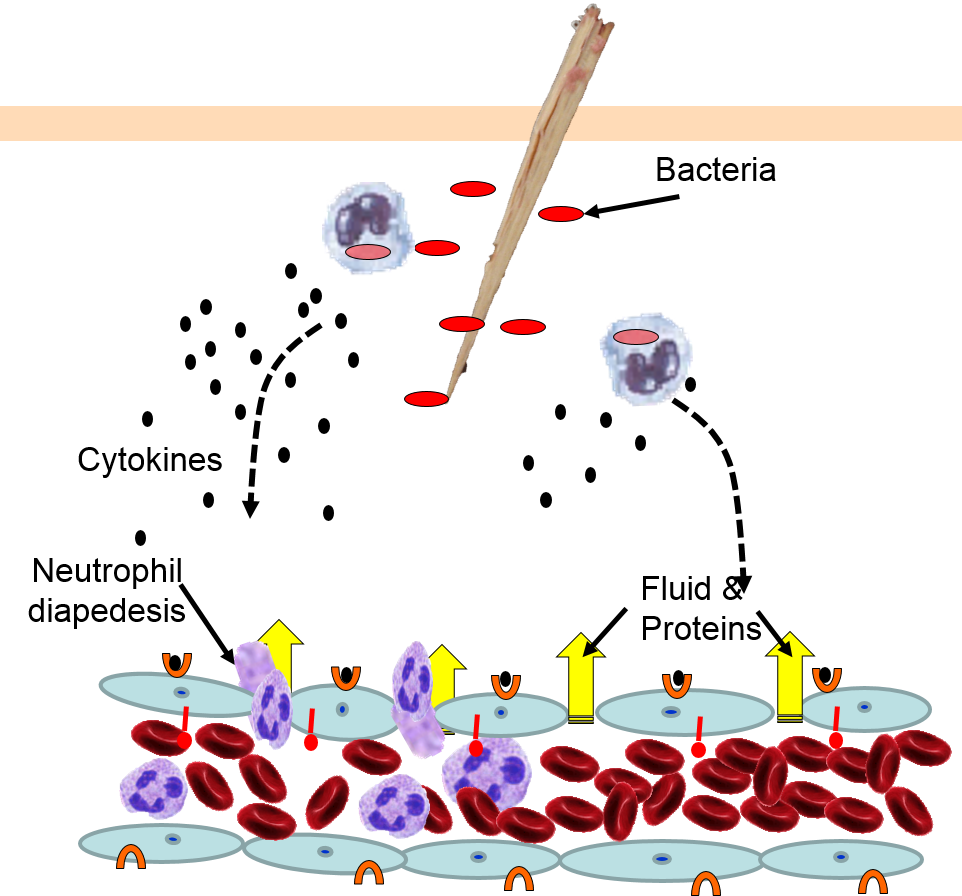
Comments
Post a Comment